[ad_1]
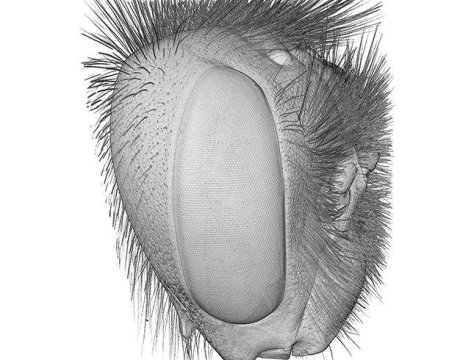
By generating 3D images of bumblebees’ compound eyes, researchers at Lund University in Sweden have discovered how bumblebees differ in their vision. The results could contribute to increased knowledge about the pollination process — once researchers are able to determine which flowers different bees see easily, and which ones they find it harder to distinguish.
Researchers have previously known that large bees see better than smaller individuals, but it has been unclear why.
“We have investigated the compound eyes of buff-tailed bumblebees of various sizes. What field of view do they have and with what resolution do they see? Now we know how large flowers need to be for individuals of various sizes to spot them. We have found out why large bumblebees see small objects better,” says Pierre Tichit, doctoral student at the Department of Biology at Lund University.
Together with Emily Baird, Gavin Taylor and colleagues from Germany and the UK, Pierre Tichit has developed a new method. Using computer-assisted tomography and very high-resolution imaging, the researchers succeeded in generating three-dimensional images of the bumblebees’ compound eyes, showing how and what they see in various parts of their field of view.
The results show that large individuals see better than small ones in certain parts of their field of vision — more specifically, in front of them and slightly above them. This could make it easier for large bees to discover flowers at a distance as well as to find small flowers. It also becomes easier for them to see hanging flowers and blooms they need to access from below.
“Our results help us understand why pollination is adversely affected if plants with larger flowers disappear in an area dominated by smaller bees. It becomes possible to do something about it,” says Emily Baird.
The next step is to use the method to compare vision in different species of bee.
“Bees are found all over the world, from the rainforest to the tundra. With our technology, we hope to be able to understand how their vision is adapted to the various environments they inhabit,” concludes Pierre Tichit.
Story Source:
Materials provided by Lund University. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
[ad_2]