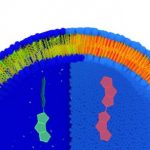
Study: Measuring the tension of a cell with a molecule — (Details)
The volume of cells can vary dramatically. Similarly to an inflating balloon, the volume increase of growing cells pushes on the plasma membrane...
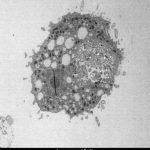
Study: How the cholera bacterium survives water predators — (Details)
The cholera-causing bacterium, Vibrio cholerae, is commonly found in aquatic environments, such as oceans, ponds, and rivers. There, the bacterium has evolved formidable...
Study: Not too long and not too short — (Details)
Researchers have found a sweet spot of six to eight hours sleep a night is most beneficial for heart health. More or less...
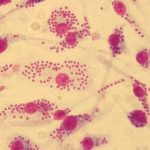
Study: Researchers in medicinal chemistry and parasitology develop an innovative strategy to identify leishmanicidal...
Leishmania is a microorganism that enters the human body via a sandfly bite. Instead of fleeing the white blood cells deployed by the...
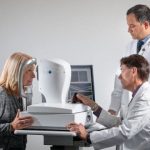
Study: Noninvasive test may screen for disease before symptoms appear — (Details)
It may be possible in the future to screen patients for Alzheimer's disease using an eye exam.
Using technology similar to what is found...
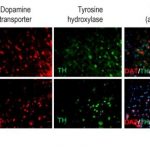
Study: New cell surface markers — (Details)
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease that affects dopamine signaling neurons in patients' brains. Cell-replacement therapy shows some promise as a treatment for...
Study: How enzyme detects ultraviolet light damage — (Details)
Damage to DNA is a constant threat to cellular life, and so it is constantly monitored and detected by a family of enzymes...
Study: How sleep loss may contribute to adverse weight gain — (Details)
In a new study, researchers at Uppsala University now demonstrate that one night of sleep loss has a tissue-specific impact on the regulation...
Study: Synchronized brain-like activity created, recorded and influenced by electrical stimulation — (Details)
Researchers in the University of Georgia's Regenerative Bioscience Center have succeeded in reproducing the effects of traumatic brain injury and stimulating recovery in...
Study: How rabies virus moves through nerve cells, and how it might be stopped...
To successfully infect its host, the rabies virus must move from the nerve ending to the nerve cell body where it can replicate.
In...
Top News
Hey ISIS, You Suck: Local Muslims Post Anti-ISIS Billboard
A new billboard on Manchester Road in Missouri reads, "HEY ISIS, YOU SUCK!!! From: #ActualMuslims."
A group of Muslim-Americans have put up a blunt billboard...